Introduction
The ABS Module within LMS is an asset-backed securities' module allowing for the management of receivables' portfolios, car leases and more. Assets can be added on an individual basis, under “Assets”, or in bulks through the asset import functionality.
Instruction videos
Asset import
Payment import
Car lease calculation
Field descriptions
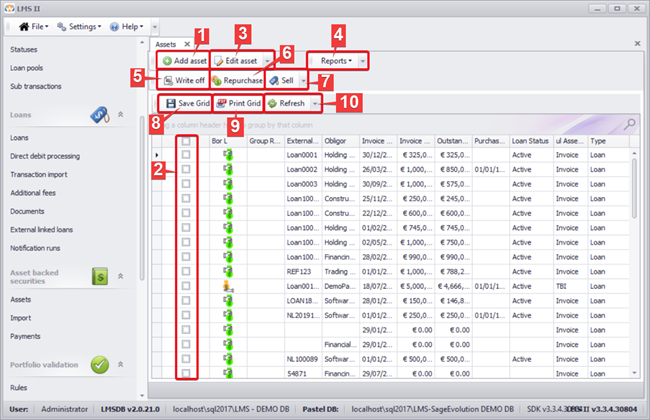
1. Asset overview
Under “Assets” in the Asset-backed securities (ABS) section an overview of all existent assets can be found. The following functions are available.
- Add asset: Using this function, new assets can be added.
- Select assets: Assets can be selected by ticking the checkbox in front of the according assets from the overview.
- Edit asset: Using this function, the selected assets (2) can be edited.
- Reports: Using this function, reports can be generated for the selected assets (2). A choice can be made between asset confirmation and asset overview (see image below).
- Write off: Using this function, the selected assets (2) can be written off.
- Repurchase: Using this function, the selected assets (2) (assets that have previously been sold) can be repurchased.
- Sell: Using this function, the selected assets (2) can be sold.
- Save grid: Using this function, the data displayed in the assets’ overview can be exported to Excel.
- Print grid: Using this function, the data displayed in the assets’ overview can be saved as PDF and/or printed directly.
- Refresh: Using this function, the data displayed in the assets’ overview can be refreshed, e.g. when recently created assets are not yet displayed in the overview.
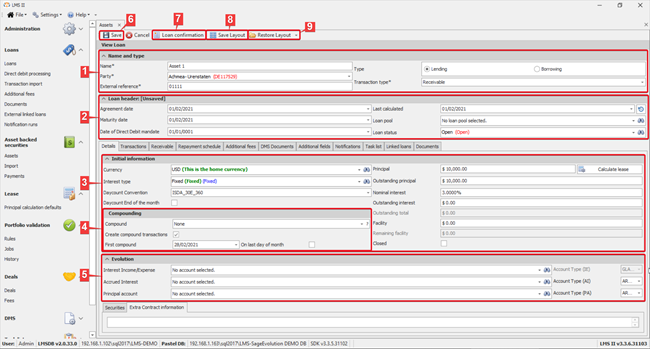
2. New asset
When creating a new loan, the following information is to be provided.
- Name and type
- Name: Name for the asset.
- Party: The party to/from which the asset is issued.
- Type: A choice can be made between lending and borrowing.
- External reference: A reference (other than the loan code, generated by the system) to be used in identifying the asset.
- Transaction type: A choice can be made between loan, receivable, car leases and originator. The asset type is to be set to “Receivable” when creating new assets.
- Note: For an asset to be saved a name, external reference and party are required. In the event that one or more of these are missing the user will be notified by the system (see image below).
- 2. Loan header
- Agreement date: Date on which the receivable is to be agreed on (the beginning of the asset term).
- Maturity date: Date on which the asset term ends.
- c. Date of direct debit mandate
- Loan status: A choice can be made between active, non-performing, open, suspended, closed, awaiting approval, fully paid, partially paid, repurchased, written off and sold.
- Last calculated: Date on which the asset was last calculated.
- Loan pool (Optional): Using this field the asset can be added to a loan pool (if any).
- 3. Initial information
- Currency: The currency of the asset (the currency in which all transactions are to be handled) is to be set.
- Interest type: A choice can be made between a fixed and other interest type(s).
- Note: Interest types can be added under Administration >> Interest types.
- Day-count convention: The day count convention to be used in calculating interest is to be selected. A choice is available between US_30_60, ICMA_30E_360, ISDA_30E_360, Actual_365_Fixed, Actual_360_Fixed, Actual_ISDA.
- Day-count end of month: This function allows for specifying whether the day-count is to be ended at month-end.
- Principal: The value of the newly created asset is to be set.
- Outstanding principal (Optional): This amount will automatically be set to the principal amount. It can, however, be modified if the two differ, e.g. if the new asset has been issued before recording it to LMS and has been partially repaid.
- Nominal interest: The nominal interest rate (per period) for the newly created asset is to be set.
- Outstanding interest (Optional): This amount will automatically be set to the interest amount. It can, however, be modified if the two differ, e.g. if the new asset has been issued before recording it to LMS and has been partially repaid.
- Facility: Using this function, a facility for the asset can be set.
- Closed: This function can be used to specify whether the recorded asset has been closed.
- 4. Compounding
- Compound: A choice can be made between none, annual, semi-annual, quarterly and monthly, depending on the compounding frequency (if any).
- Create compound transactions: This function can be used to specify whether compound transactions (if any) are to be automatically created by the system.
- First compound: The date of first compound (if any) is to be set.
- On last day of month: This function allows for specifying whether the day-count is to be ended at month-end.
- 5. Evolution
- Interest income/expense: A choice can be made for the account to be linked to the interest income/expense derived from the asset.
- Account type (IE): The account type (of the account to be linked to the interest income/expense derived from the asset) is automatically set to GL account.
- Accrued interest: A choice can be made for the account to be linked to the interest accrued from the asset.
- Account type (AI): A choice can be made for the account type (of the account to be linked to the interest accrued from the asset) between GL account, AR account and AP account.
- Principal account: A choice can be made for the account to be linked to the principal derived from the asset.
- Account type (PA): A choice can be made for the account type (of the account to be linked to the principal derived from the asset) between GL account, AR account and AP account.
- 6. Save: Using this button, the newly created asset can be saved in the system.
3. Additional fees
Under "Additional fees" fees can be added and managed. The following functions are available:
- 1. Add fee: Using this function, additional fees can be added.
- 2. Edit fee: Using this function, existing fees can be edited.
- 3. Delete fee: Using this function, existing fees can be removed from the list.
- 4. Show deleted: Using this function, the fees’ overview can be modified to also display fees that have been deleted.
- 5. Export grid: Using this function, the data, displayed in the overview, can be exported to Excel.
- 6. Refresh: Using this function, the data, displayed in the overview, can be refreshed, e.g. when a new fee has been added but it is not yet displayed in the overview.
When adding a new fee or editing an existing one, a fee code (1) and description (2) are required (see image below). A choice can be made whether fee is to be added to loans by default (3). The calculation method (4) can consist of a fixed amount or a percentage of full or outstanding principal, payment amount, or the principal repayment amount for the period to which the fee is to be applied. The "Calculation value" field (5) is to be filled in with either the fixed fee amount or the percentage (in percentage terms). Further, the recurrence of the fee (6) can be modified - a choice is available between none, repayment schedule (implying that the fee is applicable to each repayment period), monthly, quarterly, semi-annual, and annual. The fee can be designed as a charge to the lending or the borrowing party, or to both parties (7). The sub-transaction (8) and Evo integration account (9) per fee can also be selected in the according fields. the “Deleted” option (10) allows for marking a fee as removed. Finally, new fees and changes in existing ones can be saved, using the “Save” button (11).
After creating the needed fee options, the according fees can be added to each asset, using the "Add fee" button (1) under the "Additional fees" tab per asset (see image below). Per added fee the period (i.e. start and end date) to which the fee is applicable is to be set. Further, for fees with fixed amounts, a quantity of periods to which the fee is applicable, is required. Fees, already added to an asset, can be removed by selecting the according fee and using the "Remove fee" button (2).
4. Asset import
Under “Import” in the Asset-backed securities (ABS) section an overview of all previous imports can be found. The following functions are available.
- 1. Add import: Using this function, new import files can be added to the system. In doing so an import template (1) is to be selected from the list of available templates (see image below). An import date (2) and purchase date (3) are to further be set for the assets to be imported. An import transaction file in accordance with the selected import template is to be selected (4). In the event that the import file does not comply with the import template, an error message will be displayed by the system (see image on the right). The grid can be saved (5) and/or reset (6), using the according buttons. The data displayed in the transaction overview can be refreshed, suing the “Refresh” button (7). A random selection of assets to be imported from the import file can be made (8).
In adding an import file, an originator asset needs to be created to which the imported assets are to be linked.
After the file has been imported, the transactions, extracted from the import file are displayed in the overview. Transactions can be selected by ticking the checkboxes in front of the according transactions (1). The selected transactions (1) are to then be validated by using the “Validate transactions” button (2).
A message on the validation of the selected transactions will be displayed by the system.
After validation, the valid transactions can be selected by ticking the checkboxes in front of the according transactions (1) and, accordingly, processed, using the “Process” button (2).
- 2. Template editor: Using this function, new import templates can be created (1) and/or the available templates can be reviewed and modified (2). Per template a name (3), template type (4), column delimiter (8) and culture (9) are to be specified. Optionally, asset eligibility validation (5) can be selected. The “File includes header” (6) and “Is default template” (7) functions can be activated per template where applicable. New columns can be added to the template (10). Per template column, the according LMS column (11) and LMS table (12) are to be set. The columns to e required by the system (13) can be marked, and a column index (14) and import column (15) are to be provided. Additionally, the data type (16) per column is to be specified (i.e. text, number, date, true/false). A default value (17) per column can also be provided.
Import columns can be selected by ticking the checkboxes in front of the according columns (18) and removed (19). The grid, containing all the data on the created columns can also exported to Excel (20). The new template and/or the changes made to an existing one can be saved, using the “Save template” button (21). Accordingly, the template can be exported, using the “Export template” button (22), and sed in creating an import file., and sed in creating an import file., and sed in creating an import file.
5. Payments import
Similar to the asset import, multiple payments can be added through the payment batch import under “Payments”, using the “Add payment batch” button (1). Previously added batches can be edited by selecting the according batch (2) and using the “Edit payment batch” button (3). The grid, containing the batches’ details can be exported to Excel (4) and/or reset to default (5).
When importing payment batches, an import template is to be set (see previous section) and selected (1). The file can then be imported, using the “Import file” button (2).
The imported transactions can then be validated by selecting those transactions (1) and using the “Validate payments” button (2).
Once the transactions have been validated, the valid transactions can be selected (1) and processed, using the “Process payments” button (2).